Triadic Color Scheme with HSL
Color theory is a foundational element of art and design that has evolved over centuries, tracing back to the early works of artists and scientists who sought to understand the nature of light and color. The principles of color theory provide a structured approach to mixing colors and understanding their relationships, enabling artists and designers to create visually appealing and harmonious compositions.
Color theory encompasses various types of color schemes that help achieve different visual effects, such as unity, contrast, and balance. These schemes include monochromatic (using variations of a single hue), analogous (using colors next to each other on the color wheel), complementary (using colors opposite each other), and triadic (using three evenly spaced colors).
Each scheme offers unique advantages and can be used strategically to evoke specific emotions and responses in the viewer.
Understanding the Triadic Color Scheme
A triadic color scheme is a dynamic and harmonious approach to color selection, involving three colors that are evenly spaced around the color wheel. This type of scheme is particularly noted for its vibrancy and balance, making it a popular choice among designers and artists. The equal spacing of the colors ensures a pleasing contrast while maintaining harmony, preventing any single color from dominating the composition.
Common examples of triadic color schemes include the primary colors (red, yellow, blue) and the secondary colors (orange, green, purple). The primary triad is foundational in art and design, often used in early education to teach color mixing and relationships. Meanwhile, secondary triads, derived from mixing primaries, offer more complex and nuanced palettes.
The key to a successful triadic scheme lies in the careful balance of these three colors, ensuring they complement and enhance each other within a design.
HSL (Hue, Saturation, Lightness)
HSL stands for Hue, Saturation, and Lightness, and it is a color model that represents colors in a cylindrical-coordinate system. This model is widely used in design and digital art because it aligns more closely with how humans perceive colors compared to other models like RGB (Red, Green, Blue) or CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key/Black).
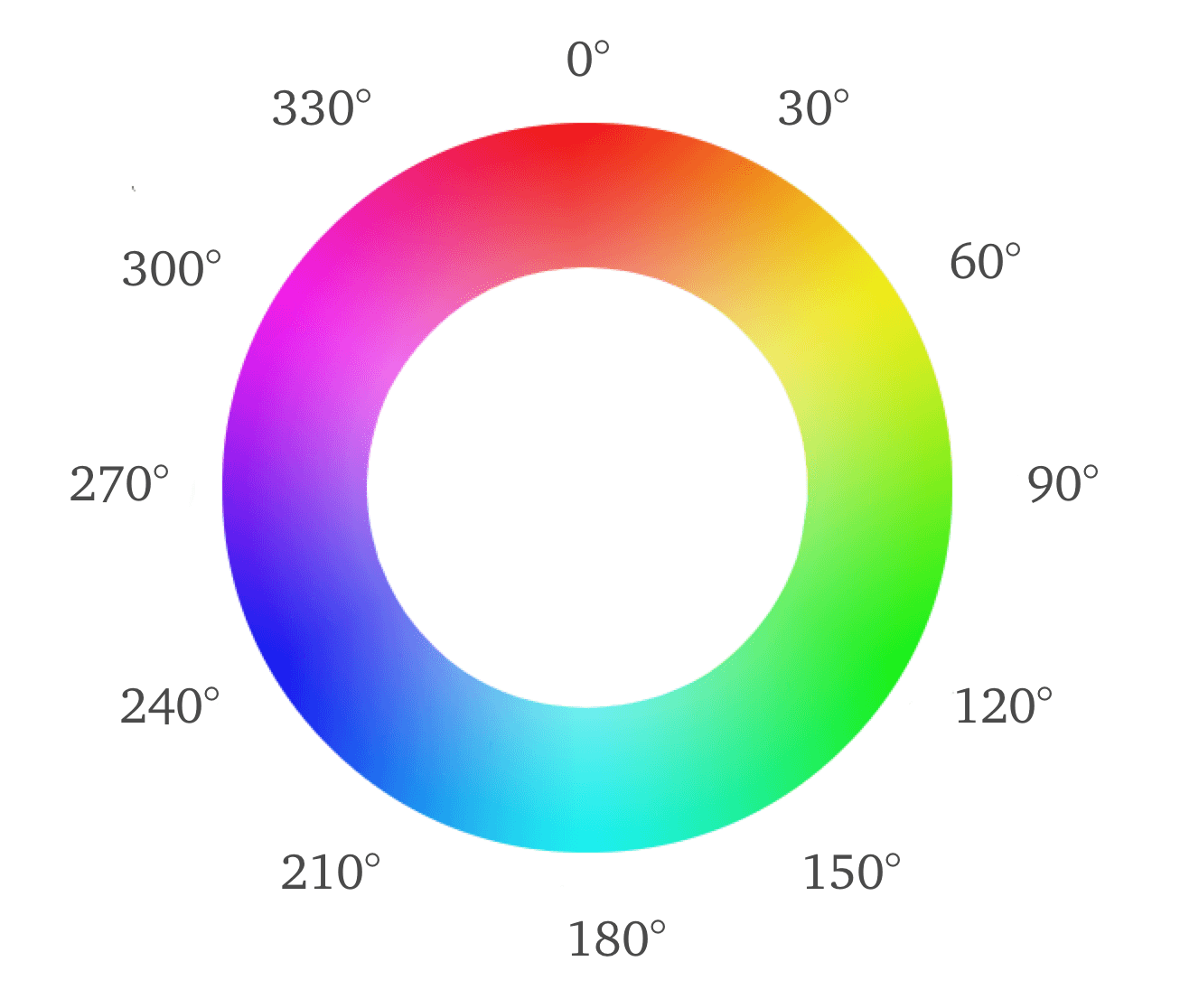
- Hue represents the type of color and is measured in degrees on a color wheel, ranging from 0° to 360°. Each degree corresponds to a specific color, with 0° being red, 120° being green, and 240° being blue, for example.
- Saturation measures the intensity or purity of the color, ranging from 0% to 100%. A saturation of 0% results in a shade of gray, while 100% represents the full, vivid color without any addition of gray.
- Lightness measures the brightness of the color, also ranging from 0% to 100%. A lightness of 0% is black, 50% is the true color at full intensity, and 100% is white.
The HSL model is particularly useful because it allows designers to intuitively adjust colors to achieve the desired look and feel by manipulating these three attributes independently.
Applying HSL to Triadic Color Schemes
Applying HSL to triadic color schemes involves selecting a base color and then finding the other two colors by adjusting the hue while keeping the saturation and lightness consistent. This method ensures that the colors are evenly spaced and maintain harmony.
Choosing a Base Color
- Setting the Hue: Start by selecting a hue for your base color. For instance, if you choose a hue of 0° (red), the other two colors in the triadic scheme will be 120° (green) and 240° (blue) around the color wheel. The key is to ensure that these hues are equidistant, maintaining the triadic relationship.
- Adjusting Saturation and Lightness: After setting the hue, fine-tune the saturation and lightness to achieve the desired intensity and brightness. For example, if you want a more subdued palette, you might reduce the saturation and lightness of all three colors evenly. Conversely, if you want a vibrant and dynamic palette, you might increase the saturation while adjusting the lightness to maintain contrast.
Finding the Triadic Colors
- Calculating the Hues: Once you have your base hue, add 120° to find the second color and another 120° for the third color. For example, with a base hue of 30° (orange), the triadic colors would be 150° (spring green) and 270° (medium slate blue). This ensures that the colors are evenly spaced and balanced.
- Maintaining Balance: It is crucial to ensure that the saturation and lightness levels are consistent across the three colors to maintain harmony. By keeping these attributes balanced, you avoid creating visual dissonance and ensure that the colors complement each other within the design.
Practical Applications of Triadic Color Schemes with HSL
Triadic color schemes using HSL can be applied effectively in various fields, offering a vibrant and balanced palette that enhances the visual appeal of any project.
Graphic Design
- Website Design: In website design, triadic color schemes can be used to create visually appealing and cohesive designs. By carefully selecting and balancing three colors, designers can ensure that different elements of the website stand out while maintaining a harmonious overall look. For instance, one color can be used for the background, another for the text, and the third for accents such as buttons and links.
- Branding and Logo Creation: Triadic color schemes are also powerful tools in branding and logo design. A well-chosen triadic palette can make a brand’s visual identity memorable and distinctive. The balanced contrast provided by the triadic scheme ensures that the logo is eye-catching without being overwhelming, which is crucial for effective brand recognition.
Interior Design
- Room Color Palettes: In interior design, triadic color schemes can be used to create lively and balanced environments. For example, in a living room, one color can be used for the walls, another for the furniture, and the third for accessories and decor items. This approach creates a cohesive and dynamic space that is visually interesting without being chaotic.
- Furniture and Decor Coordination: Triadic color schemes can also guide the selection of furniture and decor items. By choosing items that align with the triadic palette, designers can ensure that all elements of the room complement each other, creating a harmonious and inviting space.
Art and Illustration
- Painting: In painting, triadic color schemes can be used to create dynamic and balanced compositions. By carefully selecting and balancing three colors, artists can ensure that their paintings are visually appealing and harmonious. This approach can be applied to both traditional and digital painting, providing a versatile tool for artists.
- Digital Art: In digital art, triadic color schemes using HSL adjustments offer a powerful way to create vibrant and harmonious designs. Digital artists can use software tools to fine-tune the hue, saturation, and lightness of each color, ensuring a balanced and visually appealing result. This flexibility makes triadic color schemes an excellent choice for a wide range of digital art projects.
Tools and Resources for Working with Triadic Color Schemes and HSL
To effectively work with triadic color schemes and HSL, several tools and resources are available that can assist designers and artists in creating balanced and harmonious color palettes.
Online Color Palette Generators
- Adobe Color: Adobe Color is an online tool that allows you to create and save color schemes. It provides a user-friendly interface where you can explore different color relationships, including triadic schemes. You can also import images to extract color themes and use various color rules to generate harmonious palettes.
- Paletton: Paletton is another online resource for generating color palettes based on various schemes, including triadic. It offers an intuitive interface where you can experiment with different color combinations and view them in various contexts, such as web pages and artwork. This tool is particularly useful for quickly visualizing and adjusting triadic color schemes.
Software and Apps
- Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator: These professional design software tools offer advanced color management features that allow you to create and manipulate triadic color schemes using the HSL model. With precise control over hue, saturation, and lightness, you can fine-tune your color palettes to achieve the desired effect.
- Procreate: Procreate is a powerful digital illustration app that offers extensive color tools, including HSL adjustments. Artists can use Procreate to create vibrant and balanced color schemes for their digital artworks, making it a versatile tool for professional and hobbyist artists alike.
Educational Resources
- Books: Several books provide in-depth knowledge and practical guidance on color theory and its application. “Interaction of Color” by Josef Albers is a classic resource that explores the perception and interaction of colors. “Color: A Workshop for Artists and Designers” by David Hornung offers practical exercises and insights into using color effectively in art and design.
- Online Courses and Tutorials: Websites like Coursera, Udemy, and Skillshare offer a variety of courses and tutorials on color theory and design. These resources provide valuable insights and practical tips for working with triadic color schemes and the HSL model, making them accessible to learners of all levels.
Tips and Best Practices
Balancing Colors for Visual Appeal
- Use the 60-30-10 rule: This rule suggests using 60% of a dominant color, 30% of a secondary color, and 10% of an accent color. This approach helps create a balanced and harmonious composition, with the dominant color providing the base, the secondary color adding interest, and the accent color providing highlights.
- Ensure that the saturation and lightness levels are balanced to avoid overwhelming the viewer. By keeping these attributes consistent, you can create a cohesive look that is visually appealing and easy on the eyes.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Avoid using colors with drastically different saturation and lightness levels, as this can create visual discord. Instead, aim for a balance where the colors complement each other without clashing.
- Don’t rely solely on bright, saturated colors; incorporating various shades and tints can add depth and interest to your design. By experimenting with different levels of saturation and lightness, you can create a more nuanced and sophisticated palette.
Experimenting and Iterating
- Continuously test and adjust your color schemes to find the perfect balance. This iterative process allows you to refine your palette and ensure that it meets your design goals.
- Use design feedback and user testing to refine your color choices. By gathering input from others, you can gain valuable insights into how your colors are perceived and make adjustments as needed.
Conclusion
Triadic color schemes using the HSL model offer a powerful way to create balanced, vibrant, and harmonious designs. By understanding the principles of color theory and how to apply HSL, designers can craft visually appealing works in various fields, from graphic and interior design to art and illustration.
With the right color tools and resources, and by following best practices, anyone can master the use of triadic color schemes to enhance their creative projects. Embrace the vibrant world of color, experiment with different combinations, and see how triadic color schemes can transform your designs. The journey of exploring color is both exciting and rewarding, opening up endless possibilities for creative expression and visual storytelling.



